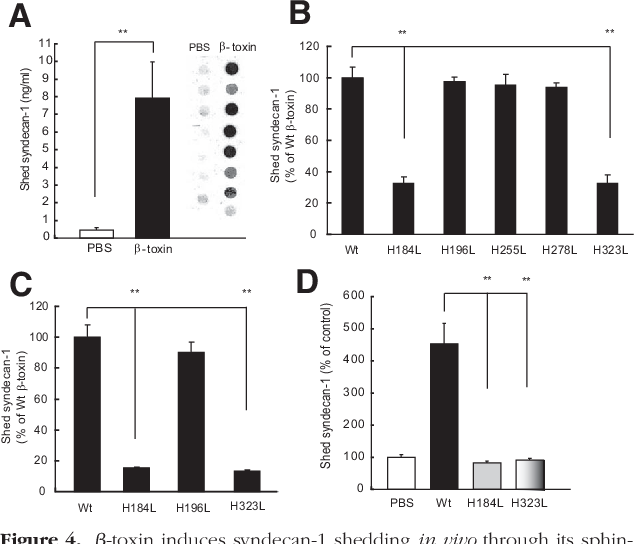
Staphylococcus aureus beta toxin is a toxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus. It is a form of sphingomyelinase called sphingomyelinase C. This enzyme is toxic to a variety of cells, including erythrocytes, fibroblasts, leukocytes, and macrophages. Susceptible cells are subject to lysis of exposed sphingomyelin on their membrane surfaces.
The beta toxin exhibits maximum activity at 10 °C, at 37 °C (normal body temperature) seems to be inactive.
References