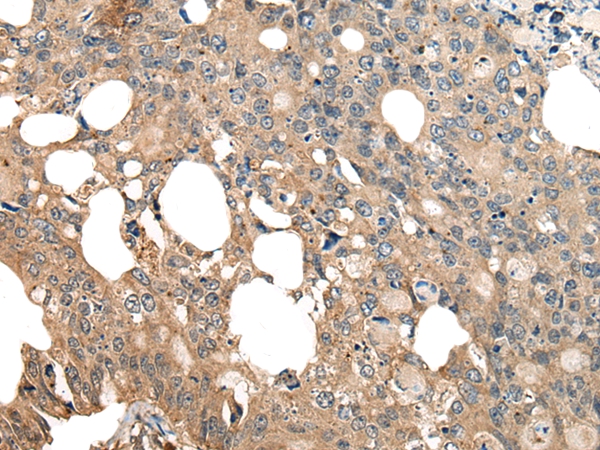
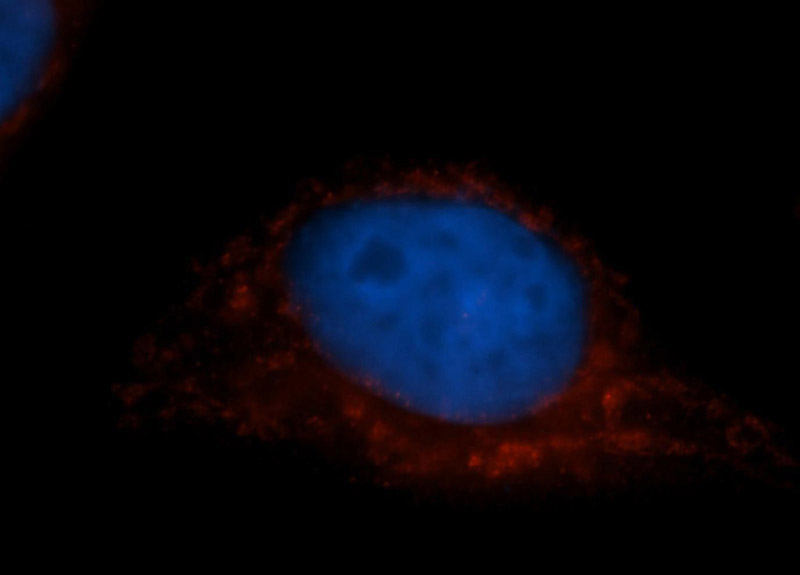
Cytochrome c oxidase polypeptide 7A2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the COX7A2 gene.
Cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, catalyzes the electron transfer from reduced cytochrome c to oxygen.
This component is a heteromeric complex consisting of 3 catalytic subunits encoded by mitochondrial genes and multiple structural subunits encoded by nuclear genes. The mitochondrially encoded subunits function in electron transfer, and the nuclear-encoded subunits may function in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This nuclear gene encodes polypeptide 2 (liver isoform) of subunit VIIa and the polypeptide 2 is present in both muscle and nonmuscle tissues.
In addition to polypeptide 2, subunit VIIa includes polypeptide 1 (muscle isoform), which is present only in muscle tissues, and a related protein, present in all tissues. This gene may have several pseudogenes.
References
External links
- Human COX7A2 genome location and COX7A2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading