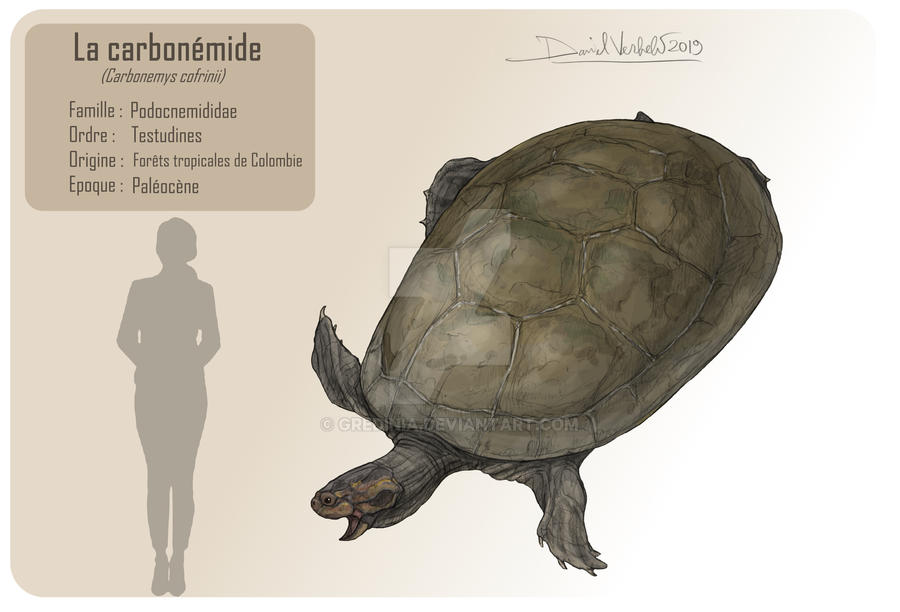
Carbonemys cofrinii is an extinct giant podocnemidid turtle known from the Middle Paleocene Cerrejón Formation of the Cesar-Ranchería Basin in northeastern Colombia. The formation is dated to approximately 60 to 57 million years ago, beginning about five million years after the KT extinction event.
Discovery and Naming
In 2005, Edwin Cadena, a doctoral student from North Carolina State University, discovered the holotype specimen in the Cerrejón coal mine. The genus name, meaning "Coal Turtle," is derived from Carbon" Latin for "coal" and "emys" Greek for "freshwater turtle," a reference to the coal mine from which the fossil was extracted. The specific epithet honors Dr. David Cofrin.
Description
The Carbonemys holotype had a shell that measured approximately 1.72 metres (5 ft 8 in), estimated at 1.8 metres (5 ft 11 in) for a complete carapace. This would place it among the one of the world's largest turtles, tied with the Quaternary Peltocephalus maturin and Eocene Drazinderetes in carapace length, and exceeded only by the Cretaceous protostegids, the Miocene Stupendemys, and two Quaternary testudines (Megalochelys and Titanochelon).
Paleobiology
Carbonemys’s relatively massive jaws suggest it possessed a powerful bite. It was likely an omnivore, consuming plants and mollusks, as well as smaller reptiles, which were diverse and abundant in its neotropical freshwater habitat. Its cohabitants included other turtles like the smaller podocnemid Cerrejonemys, giant boid (constrictor) Titanoboa, and crocodylomorphs such as the dyrosaurids Cerrejonisuchus, Acherontisuchus, and Anthracosuchus.
References