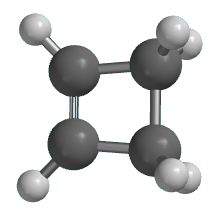
Cyclobutene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C4H6. It is a cycloalkene. It is a colorless gas that easily condenses. It is of interest in research but currently has no practical applications. A modern synthesis involves the 2-step dehydration of cyclobutanol. The compound was first prepared by thermolysis of the ammonium salt [C4H7N(CH3)3]OH (cyclobutyltrimethylammonium hydroxide).
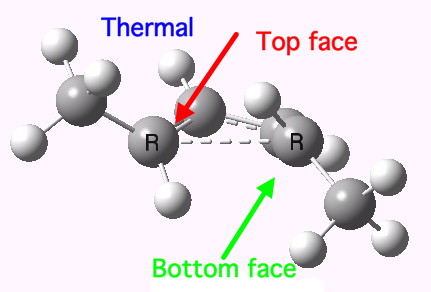
Cyclobutene thermally isomerizes to 1,3-butadiene. This strongly exothermic reaction reflects the dominance of ring strain. In contrast, the corresponding equilibrium for hexafluorocyclobutene disfavors hexafluorobutadiene.
See also
- Cyclobutane
- Cyclobutadiene
- Cyclobutyne
- Squaric acid
References